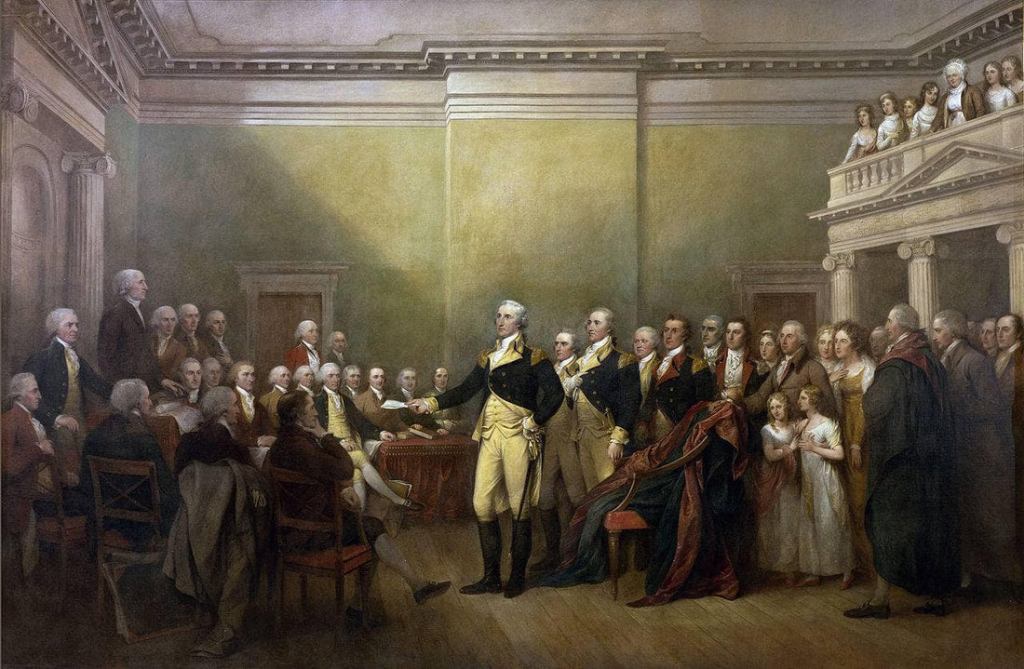
Painting: John Trumbull. George Washington resigns as Commander-in-Chief, Continental Army.

I grew up in an America that celebrated George Washington’s February 22 birthday as a national holiday, signed into law by President Rutherford B. Hayes in 1879 as a federal workers’ holiday, then extended nationally in 1885.
Things changed in 1968 when Congress passed the Uniform Monday Holiday Act, providing longer weekends and consolidating observances. Washington’s Birthday was reassigned to the third Monday in February, still legally designated as his birthday, though some congressional members proposed including Lincoln’s February 12 birthday under the broader aegis of Presidents’ Day.
That broader title caught on. Retailers and state governments increasingly adopted “Presidents’ Day.” Like so many holidays, it became a corporate sales opportunity.
Accordingly, the first item in my email this morning was a Presidents’ Day furniture sale—the first of what will no doubt be a barrage as the third Monday approaches.
Historian Jonathan Horn finds it absurd that we no longer distinctly celebrate Washington’s Birthday, given that it was observed in the young nation even before the framers of the Constitution met in 1787 (“Just Call It Washington’s Birthday,” Free Press, Feb. 11, 2026).
We owe much to this exemplary leader. Ken Burns credits Washington as “the glue that held it all together” in his PBS documentary The American Revolution. Facing superior, disciplined British forces, Washington understood that victory would require patience: knowing when to retreat, striking unexpectedly, and prolonging the war.
After defeats in New York, expiring enlistments, and desertions, matters reached their nadir during the winter encampment at Valley Forge outside British-occupied Philadelphia in 1777. Starvation loomed. Smallpox ravaged the ranks. Soldiers were unpaid, underfed, and poorly clothed.
With sagacity, Washington enlisted the Prussian officer Baron von Steuben, who molded the army into a disciplined fighting force. Recruits followed in greater numbers.
After General Gates’ victory at Saratoga, Washington was able to engage French support, working through liaison with the Marquis de Lafayette.
The decisive blow came when French naval forces blocked Cornwallis’s escape at Yorktown. Washington had deceived Cornwallis into believing New York was his objective while covertly moving his troops south. The British capitulated, leading ultimately to peace in 1783.
Washington had endured criticism without vindictiveness, even surviving a mutiny threat by disgruntled, unpaid officers.
For Burns, Washington’s greatest moment was not Yorktown or Trenton, but his resignation of his commission in Annapolis in 1783. As Burns tells it, he “knew how to defer to Congress, knew how to inspire ordinary people in the dead of night, knew how to pick subordinate talent—just had a kind of presence to him that, without him, we don’t have a country” (Chadwick Moore, New York Post, Nov. 11, 2025).
He did something similar in refusing a third presidential term. His 1796 Farewell Address remains prescient in its warnings against partisanship, permanent foreign alliances, sectionalism, and constitutional usurpation: “Let there be no change by usurpation; for though this, in one instance, may be the instrument of good, it is the customary weapon by which free governments are destroyed.”
Yet Washington has come under fierce attack, criticized for slave holding and judged by contemporary moral standards. Some view him primarily as a symbol of racial oppression and seek removal of his name and likeness from public spaces.
In the aftermath of George Floyd’s killing in 2020 and the ensuing unrest, efforts accelerated to eliminate reminders of racial injustice, including monuments to Washington, Jefferson, Lincoln, Theodore Roosevelt, and Woodrow Wilson. Streets, buildings, and schools were renamed; statues toppled or defaced.
In Portland in 2020, protesters toppled and defaced a statue of Washington in a public park.
At the University of Washington, protesters called for removal of his statue.
In 2020, a statue of Washington at George Washington University was beheaded.
In 2021, the San Francisco Board of Education voted to rename a school honoring Washington, later reversing course after public scrutiny.
A Washington, D.C. working group, commissioned amid racial justice protests, recommended reviewing public names and monuments, suggesting federal sites be reconsidered for contextualization or renaming.
While some of this fury can be understood as anger over longstanding injustice, historian Howard Zinn argues in A People’s History of the United States that Washington’s mythic stature obscures his slaveholding and his violent campaigns against Indigenous peoples. Jill Lepore, in These Truths, likewise underscores the inseparability of his leadership from slavery.
It is painful to read, but much rings true.
Burns recounts Washington’s 1779 campaign against the Iroquois, ordering the destruction of settlements in retaliation for their alliance with the British: “Lay waste all the settlements around… that the country may not be merely overrun, but destroyed.” Towns and crops were burned. Many perished in the ensuing winter from famine and disease.
America was founded on a compromise that would lead to civil war and immense loss of life. Our history is marked by both courage and cruelty, liberty and bondage. We diminish ourselves if we pretend otherwise.
But we also diminish ourselves if we forget the magnitude of what was achieved: a fragile republic wrested from empire, sustained not by perfection but by discipline, restraint, and the voluntary surrender of power.
We are a nation still struggling to reconcile our ideals with our conduct. The work of ordered liberty, of constitutional self-government, of moral reckoning without erasure, remains unfinished.
The Revolution continues—not in the toppling of statues or canceling history, but by whether we can tell the truth about our past without losing the capacity to honor it.
—rj